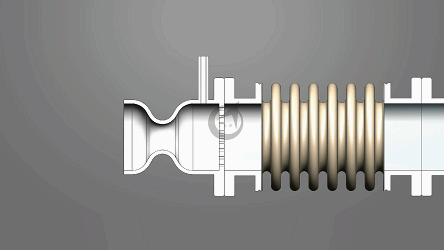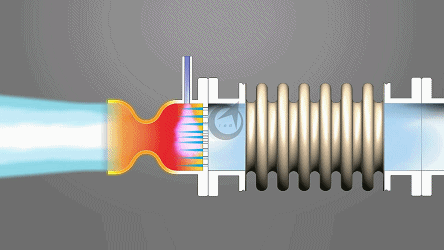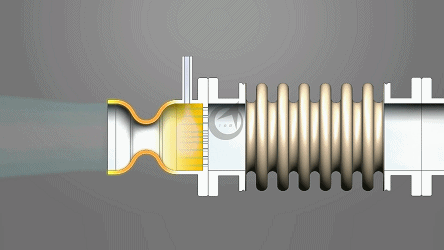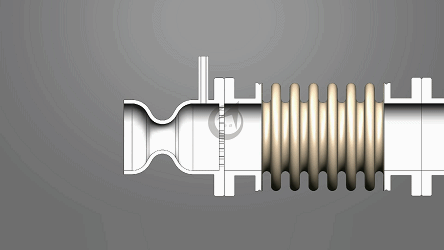
Angle compensator: Accurate and stable assurance
Release time:
2025-06-04
Angle compensator, as its name suggests, its core function is to compensate for angles. In some complex mechanical structures, due to manufacturing errors, assembly errors, or deformation under force during operation, angular deviations often occur. For example, in the construction of large bridges, if there is a slight angular deviation in the connection of the steel beams of the bridge, this deviation may continue to expand over time and under external forces, affecting the overall structural stability of the bridge.
Angle compensators play a crucial role in numerous engineering and mechanical applications. This unique device, though seemingly small, has a significant and undeniable impact.
As its name suggests, the core function of an angle compensator is to compensate for angular deviations. In complex mechanical structures, angular discrepancies often arise due to manufacturing errors, assembly errors, or deformation under stress during operation. For example, in large-scale bridge construction, even slight angular deviations in the connection of steel beams can expand over time under external forces, affecting the overall structural stability of the bridge. An angle compensator can detect these deviations and compensate for the angle through its own adjustment mechanism, ensuring that the connection angle between the steel beams remains within a reasonable range, thus guaranteeing the safety of the bridge.
In the aerospace field, the importance of angle compensators is self-evident. Precise angle control is required for aircraft wings, tail wings, and other components during flight. As external factors such as flight altitude, speed, and airflow change, the ideal angles of these components will also change. The angle compensator can compensate for these angular changes in real time, ensuring the stability of the aircraft's flight attitude. This is not only related to flight comfort but is also a key factor in flight safety. If the angle compensator malfunctions, the aircraft's flight attitude may become uncontrollable, leading to serious flight accidents.
Angle compensators also play a positive role in the automated production lines of industrial manufacturing. Various robotic arms require precise angular positioning when performing material handling, assembly, and other operations. Due to different product specifications and production task requirements, the angle of the robotic arm needs to be flexibly adjusted. The angle compensator can provide the robotic arm with fast and accurate angle compensation, improving production efficiency and product quality.
In principle, angle compensators adjust angles through hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric drives. Their internal control system can quickly calculate the detected angular deviation based on preset parameters and issue instructions to drive the compensation mechanism.
With continuous technological advancements, angle compensators are developing towards higher precision, smaller size, and stronger adaptability. New materials and advanced manufacturing processes enable angle compensators to operate in more harsh environments, such as high temperature, high pressure, and strong corrosion. Simultaneously, intelligent angle compensators can be deeply integrated with the entire equipment control system to achieve remote monitoring and automatic fault diagnosis.





 中文版
中文版