Flexible adjustment in precision engineering of angle compensators
Release time:
2025-05-14
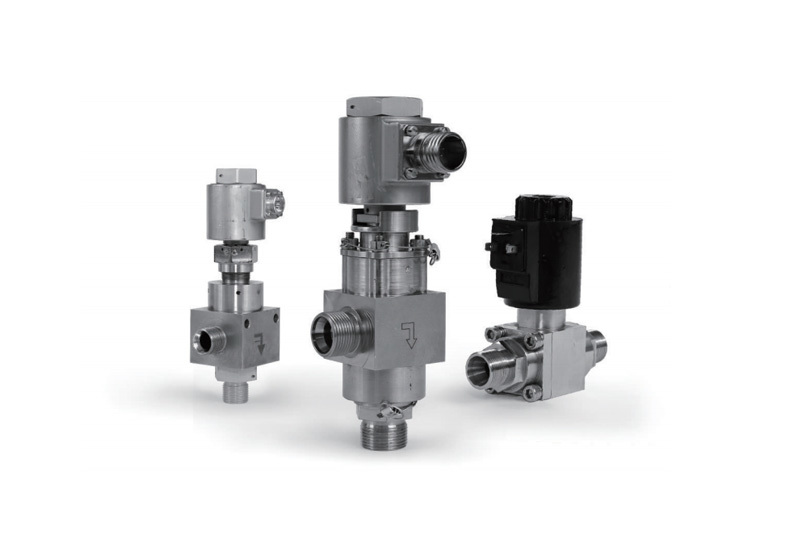
Angle compensators, as crucial components in mechanical engineering and piping systems, absorb and compensate for angular deviations in equipment or pipelines caused by temperature changes, mechanical vibrations, or installation errors, ensuring the stable and safe operation of the system. Their design integrates principles of precision mechanics and materials science, and they are widely used in aerospace, shipbuilding, energy and power, and building construction, making them indispensable flexible connection devices in modern industry.
Angle compensators, as crucial components in mechanical engineering and piping systems, absorb and compensate for angular deviations caused by temperature changes, mechanical vibrations, or installation errors in equipment or pipelines, ensuring the stability and safety of system operation. Their design integrates precision mechanical principles and materials science, and they are widely used in aerospace, shipbuilding, energy, power, and building construction, becoming indispensable flexible connection devices in modern industry.
I. Structure and Working Principle
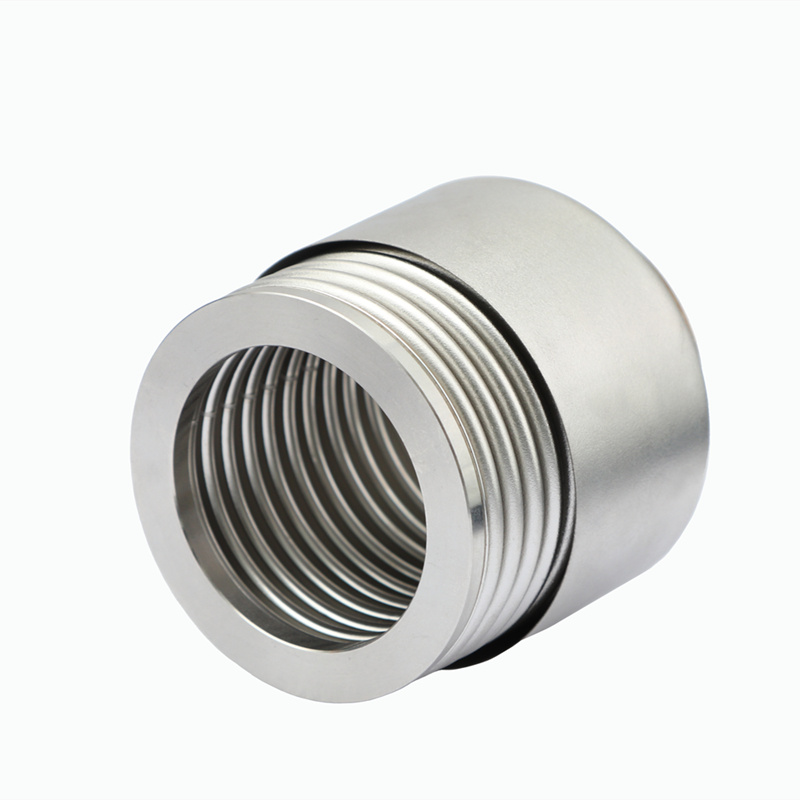
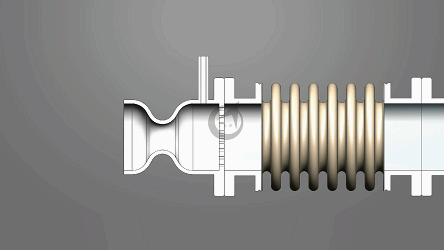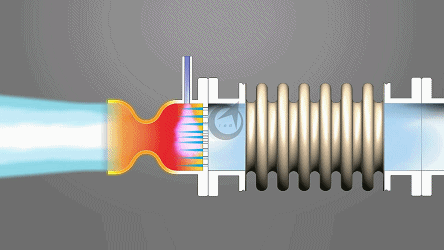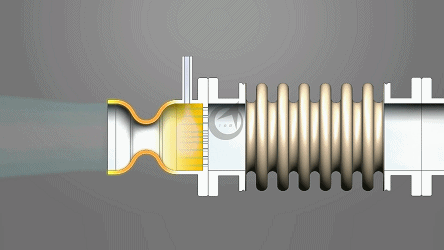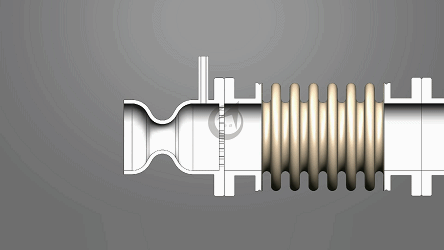
Angle compensators typically consist of bellows, connecting pipes, flanges, and guide brackets. The bellows, as the core elastic element, compensates for angular deviations through its expandable corrugated structure. When the system undergoes displacement due to thermal expansion and contraction or mechanical vibration, the bellows absorbs energy through elastic deformation, while the rigid connection of the connecting pipes and flanges ensures the stability of torque transmission. Some models are also equipped with limit devices, using mechanical limits or hydraulic damping technology to prevent the compensator from failing due to excessive deformation, significantly improving equipment life.
II. Core Performance Indicators
Compensation Capacity: Depending on the application scenario, angle compensators need to have different deflection angle ranges. For example, shipbuilding pipeline systems need to adapt to ±15° dynamic offsets, while compensators in precision instruments may only need ±0.5° fine-tuning capability.
Fatigue Life: Under cyclic loading, the bellows of the compensator must withstand tens of thousands or even millions of elastic deformations. Optimizing material selection and heat treatment processes can significantly improve its fatigue resistance.
Sealing Performance: Using metal seals or flexible graphite gaskets ensures leak-free operation in high-pressure or high-temperature environments, meeting the stringent requirements of nuclear power and chemical industries.
Corrosion Resistance: For marine environments or strong corrosive media, the compensator surface can be plated or lined with polytetrafluoroethylene technology to extend its service life.
III. Typical Application Scenarios
Aerospace: At the connection between the aircraft engine and the fuselage, the angle compensator must withstand high-frequency vibration and extreme temperature differences, while ensuring the sealing of the fuel lines.
Shipbuilding Engineering: In the low-temperature pipeline system of LNG carriers, the compensator must operate in a liquid nitrogen environment of -163°C, using a multi-layer bellows structure to compensate for thermal stress.
Energy and Power: In the main steam pipelines of ultra-supercritical thermal power units, the compensator must withstand high temperatures and pressures, and the guide brackets limit lateral displacement to ensure pipeline safety.
Building Structures: In large-span spatial structures, compensators are used to absorb structural deformations caused by earthquakes or wind loads, protecting the main structure from damage.
IV. Selection and Installation Points
Selection Criteria: The type of compensator should be selected based on the medium temperature, pressure, corrosiveness, and displacement. For example, metal bellows compensators are recommended for high-temperature environments, while non-metallic compensators are required for strongly corrosive media.
Installation Standards: Before installation, check whether the compensator model and pipeline parameters match, and ensure that the flange parallelism error is ≤0.5mm. During installation, avoid spattering welding slag damaging the bellows, and set fixed brackets to withstand internal pressure thrust.
Maintenance: Regularly check the compensator for cracks or corrosion, and verify the sealing performance through hydraulic testing. For critical equipment, it is recommended to conduct a comprehensive inspection every 3 years.
Angle compensators, as "flexible joints" in modern industry, their performance directly affects the reliability and safety of the system. Through reasonable selection, standardized installation, and regular maintenance, their compensating function can be fully utilized, providing solid protection for equipment operation under complex conditions.





 中文版
中文版